Product Details
Appearance:solid
Lidocaine belongs to the family of medicines called local anesthetics. This medicine prevents pain by blocking the signals at the nerve endings in the skin. This medicine does not cause unconsciousness as general anesthetics do when used for surgery. Shanghai Upbio Tech Co.,Ltd (Former Onchem (China)Co.,Ltd) is a comprehensive manufacturer and an international distribution of chemicals throughout the world, The predecessor of Shanghai Upbio Tech Co.,Ltd was Onchem (China) Co.,Ltd in 2010,Specialized in APIs, chemical intermediates, herbal extract and pharmaceutical raw materials.
Good Supplier In China Hot Sale Lidocaine 137-58-6 in stock
- Molecular Formula:C14H22N2O
- Molecular Weight:234.341
- Appearance/Colour:solid
- Vapor Pressure:4.28E-05mmHg at 25°C
- Melting Point:66-69 °C
- Refractive Index:1.5110 (estimate)
- Boiling Point:350.8 °C at 760 mmHg
- PKA:pKa 7.88(H2O)(Approximate)
- Flash Point:166 °C
- PSA:32.34000
- Density:1.026 g/cm3
- LogP:2.65670
Hot Sale 137-58-6
Lidocaine is a safe and effective treatment for the temporary relief of pain when its used as directed. It is also a drug widely used as the first choice drug for treating premature contractions, acute myocardial infarction, and ventricular arrhythmia associated with cardiac surgery. When used sparingly and as directed, topical lidocaine is generally safe. However, misuse, overuse, or overdose can lead to a number of serious health problems and even death. Ingestion of lidocaine can cause numbness of the mouth and throat, which can lead to trouble swallowing and even choking.
Definition
ChEBI: Lidocaine is the monocarboxylic acid amide resulting from the formal condensation of N,N-diethylglycine with 2,6-dimethylaniline. It has a role as a local anaesthetic, an anti-arrhythmia drug, an environmental contaminant, a xenobiotic and a drug allergen. It is a monocarboxylic acid amide, a tertiary amino compound and a member of benzenes. It derives from a glycinamide.
InChI:InChI=1/C14H22N2O/c1-5-16(6-2)10-13(17)15-14-11(3)8-7-9-12(14)4/h7-9H,5-6,10H2,1-4H3,(H,15,17)/p+1
137-58-6 Relevant articles
LidocAine Versus Opioids In MyocarDial infarction: the AVOID-2 randomized controlled trial
Himawan Fernando, Ziad Nehme, Catherine Milne, Jessica O’Brien, Stephen Bernard, Michael Stephenson, Paul S Myles, Jeffrey Lefkovits, Karlheinz Peter, Angela Brennan, Diem Dinh, Emily Andrew, Andrew J Taylor, Karen Smith, Dion Stub
,European Heart Journal. Acute Cardiovascular Care, Volume 12, Issue 1, January 2023, Pages 2–11
IV Lidocaine did not meet the criteria for non-inferiority with lower prehospital pain reduction than fentanyl but was safe and better tolerated as analgesia in ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI). Future trials testing non-opioid analgesics in STEMI and whether opioid avoidance improves clinical outcomes are needed.
Multicomponent Synthesis of Lidocaine at Room Temperature
Michelle Lee, Nathan J. Vosburg, Emily A. Shimizu, Manuel A. Rentería-Gómez, Rocío Gámez-Montaño, and David A. Vosburg
Journal of Chemical Education 2022, 99, 6, 2399–2402
Students also evaluated multiple lidocaine synthesis procedures using green chemistry principles and explored the reaction mechanisms of both traditional (N-acylation followed by N-alkylation) and multicomponent lidocaine syntheses.
Pressure effect on lidocaine conformational equilibria in scCO2: A study by 2D NOESY
I.A. Khodov, K.V. Belov, A.A. Dyshin, M.A. Krestyaninov, M.G. Kiselev
Journal of Molecular Liquids Volume 367, Part B, 1 December 2022, 120525
The work reports the results of an analysis of the lidocaine molecule conformational behavior in a supercritical carbon dioxide medium. Based on the nuclear Overhauser effect spectroscopy (2D NOESY) data, the authors determine the fractions of lidocaine molecule conformers in scCO2 at temperatures and pressures exceeding the critical point (308.15 K; 10–20 MPa). The paper also shows the effect of conformational inversion for this system at 308.15 K and 22 MPa. Since lidocaine polymorphic transformations can be accompanied by changes in the molecule conformation in the crystal elemental unit cell, it is quite urgent to determine the conformer fractions of this compound.
137-58-6 Upstream products
-
109-89-7
diethylamine
-
1131-01-7
2-chloro-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)acetamide
-
3734-33-6
denatonium benzoate
-
87-62-7
2,6-dimethylaniline
137-58-6 Downstream products
-
24003-58-5
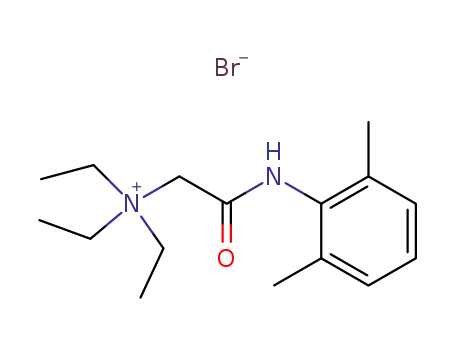
Lidocaine N-ethyl bromide
-
5369-03-9
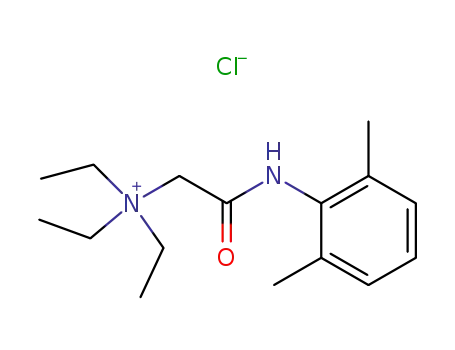
QX-314
-
2903-45-9
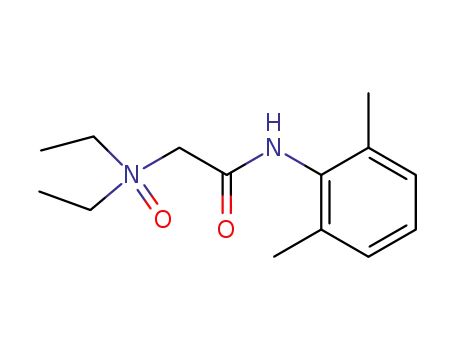
lidocaine N-oxide
-
75889-35-9
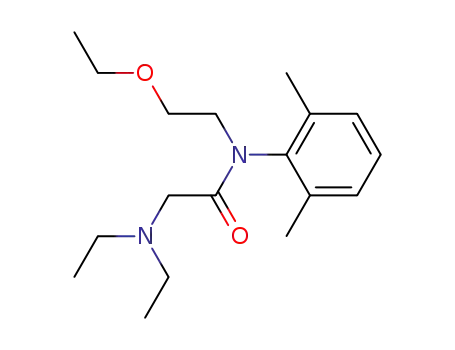
2-Diethylamino-N-(2,6-dimethyl-phenyl)-N-(2-ethoxy-ethyl)-acetamide
Relevant Products
-
Cyclopropane, isocyanato- 4747-72-2
CAS:4747-72-2
-
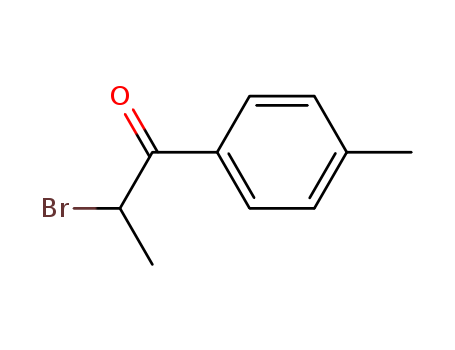
2-Bromo-4'-Methylpropiophenone
CAS:1451-82-7
-
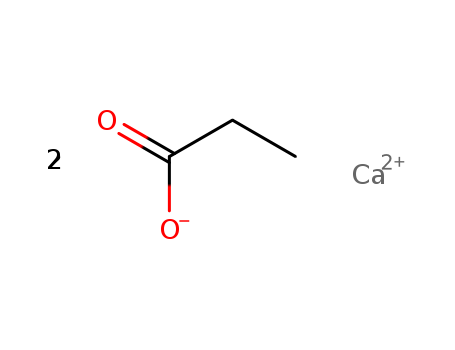
Calcium propionate, calcium salt (2:1)
CAS:4075-81-4