Product Details
Appearance:White crystalline powder
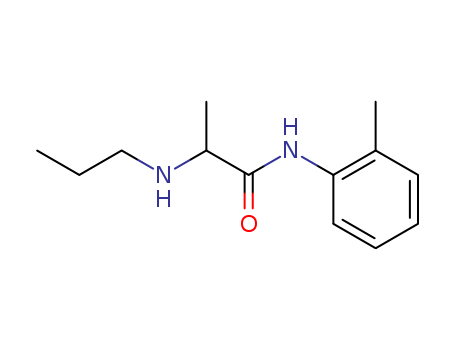
Hot Sale, best quality Prilocaine 721-50-6
- Molecular Formula:C13H20N2O
- Molecular Weight:220.315
- Appearance/Colour:White crystalline powder
- Melting Point:37-38oC
- Refractive Index:nD20 1.5298
- Boiling Point:361.6 °C at 760 mmHg
- PKA:pKa 7.32 or 7.89 (Uncertain)
- Flash Point:134.3 °C
- PSA:41.13000
- Density:1.029 g/cm3
- LogP:2.78550
top purity Prilocaine 721-50-6 Usage
Prilocaine is a secondary amide analogue of lidocaine, belongs to amide local anesthetic drug with its anesthesia intensity and speed being similar as lidocaine, which is clinically for local anesthesia, especially suitable for treating patients who are not allowed to use adrenaline. It has a better clinical performance in terms of providing rapid dental anesthesia and earlier teeth extraction than lidocaine.
Definition
ChEBI: An amino acid amide in which N-propyl-DL-alanine and 2-methylaniline have combined to form the amide bond; used as a local anaesthetic.
InChI:InChI=1/C13H20N2O/c1-4-9-14-11(3)13(16)15-12-8-6-5-7-10(12)2/h5-8,11,14H,4,9H2,1-3H3,(H,15,16)
721-50-6 Relevant articles
Prilocaine: Mechanisms and application
Naresh Kumar Katari , Sreekantha B. Jonnalagadda
Treatments, Mechanisms, and Adverse Reactions of Anesthetics and Analgesics 2022, Pages 151-164
This review describes the physical and chemical characteristics of prilocaine, and different liposomes loaded with prilocaine, their antibacterial activity, and clinical aspects of intrathecal prilocaine.
Thermal investigation on hydrated co-amorphous systems of nicotinamide and prilocaine
Xiaoyue Xu, Thomas Rades, Holger Grohganz
European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics Volume 186, May 2023, Pages 1-6
Recent studies showed that water can also act as an anti-plasticizer that reduced the molecular mobility of prilocaine (PRL), resulting in a higher Tg of hydrated PRL compared with that of anhydrous, amorphous PRL [14], [15]. The nature of the anti-plasticizing effect has not been finally elucidated, but it is speculated to be due to the interaction of water with the dimer structure of PRL [14].
721-50-6 Process route
-

- 107-10-8,42939-71-9
propylamine
-
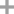
- 7623-09-8
2-chloropropionyl chloride

-
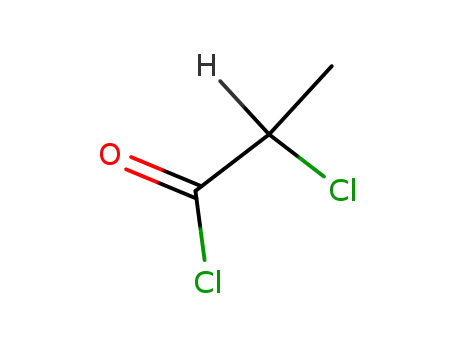
- 95-53-4
o-toluidine

-
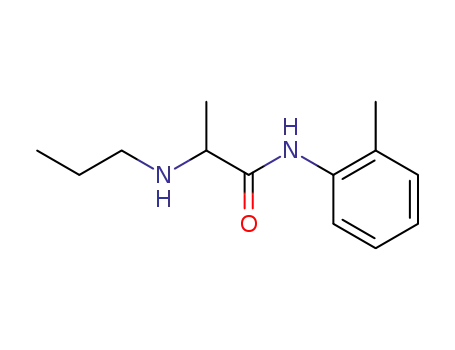
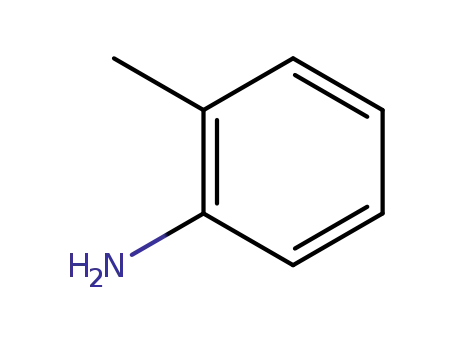
- 721-50-6,14289-31-7
prilocaine
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
2-chloropropionyl chloride; o-toluidine; With potassium carbonate; In acetone; at 0 - 30 ℃; for 5h;
propylamine; In acetone; at 70 ℃; for 14h;
|
97% |
-

- 107-10-8,42939-71-9
propylamine

-
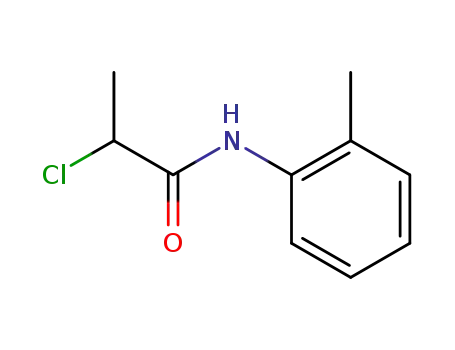
- 19281-31-3
N-(2-methylphenyl)-2-chloropropanamide

-

- 721-50-6,14289-31-7
prilocaine
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With potassium carbonate; In acetone; Reflux;
|
90% |
721-50-6 Upstream products
-
107-10-8

propylamine
-
19281-31-3

N-(2-methylphenyl)-2-chloropropanamide
-
7623-09-8

2-chloropropionyl chloride
-
95-53-4

o-toluidine
721-50-6 Downstream products
-
521964-99-8
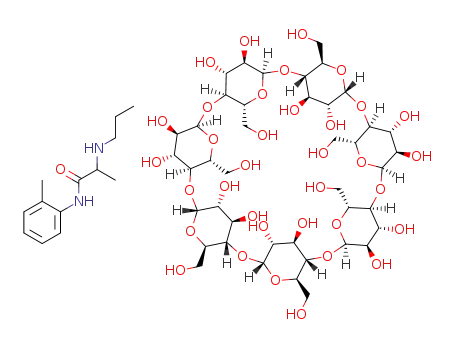
C42H70O35*C13H20N2O
-
1786-81-8
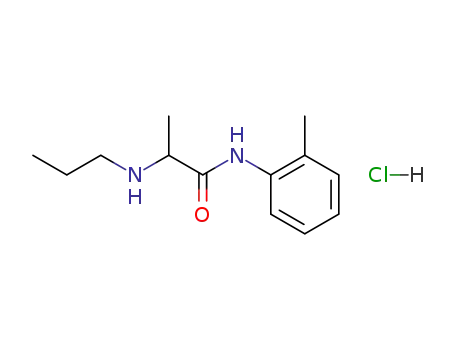
prilocaine hydrochloride
-
14289-31-7
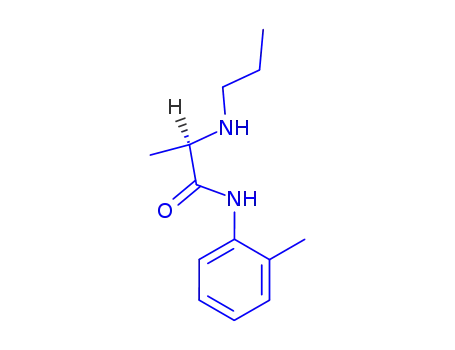
D(-)-α-Propylamino-2-methyl-propioanilid
-
14289-31-7
L(+)-α-Propylamino-2-methyl-propioanilid
Relevant Products
-
Cyclopropane, isocyanato- 4747-72-2
CAS:4747-72-2
-
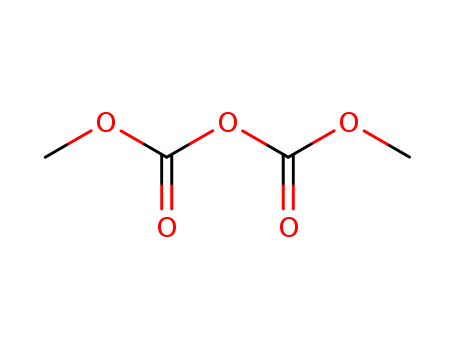
Dimethyl dicarbonate(DMDC)
CAS:4525-33-1
-
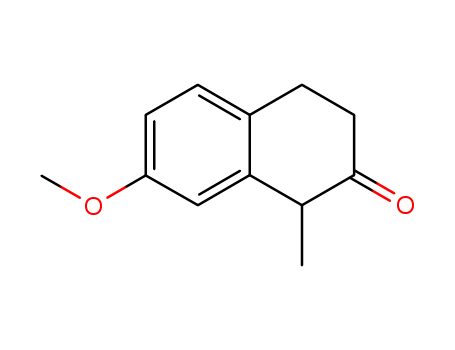
2(1H)-Naphthalenone, 3,4-dihydro-7-methoxy-1-methyl-
CAS:1204-23-5