Product Details
Appearance:Off-white powder
Hot Sale Melatonine 73-31-4 trader with best price
- Molecular Formula:C13H16N2O2
- Molecular Weight:232.282
- Appearance/Colour:Off-white powder
- Vapor Pressure:1.25E-10mmHg at 25°C
- Melting Point:116.5-118 °C(lit.)
- Refractive Index:1.6
- Boiling Point:512.831 °C at 760 mmHg
- PKA:16.26±0.46(Predicted)
- Flash Point:263.951 °C
- PSA:54.12000
- Density:1.175 g/cm3
- LogP:2.24600
Melatonine Usage
Melatonin is a hormone secreted by the pineal gland in accordance with the circadian rhythm when the light level decreases. It is a naturally compound found in animals, plants, and microbes and it is a hormone secreted by the pineal gland. The chemical structure of Melatonin was 5-methoxy-N-acetyl tryptamine, the physiological function of inhibiting gonad, thyroid, adrenal gland, parathyroid gland and pituitary function, inhibit precocious puberty, reduce pituitary Melanotropin secretion; and has a central nervous system function, can improve the convulsion the threshold, cause drowsiness. It is produced by the pineal gland in the brain and is secreted when the body recognizes darkness. Melatonin has intense effects on the timing of the sleep/awake cycle, regulating the circadian rhythms of several biological functions.
Uses
1. Melatonin can be used as medicine health care products, so as to enhance people’s immune function, preventing aging and back to youth. What’s more, it is also a kind of natural “sleeping pill”.
2. Melatonin is a kind of hormone secreted by pineal body of pituitary gland in the body. The amount of melatonin has something to do with light. The weaker the light is, the more the melatonin is, whereas the less. In addition, it is helpful to one’s sleep.
3. Biochemical research.
Definition
ChEBI: A member of the class of acetamides that is acetamide in which one of the hydrogens attached to the nitrogen atom is replaced by a 2-(5-methoxy-1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl group. It is a hormone secreted by the pineal gland in humans.
World Health Organization (WHO)
Melatonin is mainly produced by the pineal gland and secreted into the blood, which is a hormone that your brain produces in response to darkness. It is promoted as a cure for travel sickness, jet-lag and insomnia and has recently been claimed in the United States to reverse the ageing process. A synthetic version has been freely available from health food shops and pharmacies as a "nutritional supplement" since 1993.
InChI:InChI=1/C13H16N2O2/c1-9(16)14-6-5-10-8-15-13-4-3-11(17-2)7-12(10)13/h3-4,7-8,15H,5-6H2,1-2H3,(H,14,16)
73-31-4 Relevant articles
Melatonin and Health: Insights of Melatonin Action, Biological Functions, and Associated Disorders
Sheikh Bilal Ahmad, Aarif Ali, Midhat Bilal, Shahzada Mudasir Rashid, Amir Bashir Wani, Rahil Razak Bhat & Muneeb U. Rehman
Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology (2023)
Melatonin is a ubiquitous molecule with wide distribution in nature and is synthesized by animals, humans, plants, fungi, and unicellular organisms. A novel clinical area has been formed with the development of new melatonin agonists as they possess better pharmacokinetics.
Benefits of the Neurogenic Potential of Melatonin for Treating Neurological and Neuropsychiatric Disorders
Yaiza Potes ,Cristina Cachán-Vega ,Eduardo Antuña ,Claudia García-González ,Nerea Menéndez-Coto ,Jose Antonio Boga ,José Gutiérrez-Rodríguez ,Manuel Bermúdez ,Verónica Sierra ,Ignacio Vega-Naredo ,Ana Coto-Montes andBeatriz Caballero
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24(5), 4803
Melatonin (N-acetyl-5-methoxytryptamine) is a multifunctional hormone naturally produced and released rhythmically throughout the night by the pineal gland to regulate sleep–wake cycles. Melatonin treatments may improve neurobehavioral outcomes as well as motor and cognitive functions (e.g., learning and memory processes). Depending on the specific neurologic pathology, melatonin may revert and/or, at least, delay those alterations that affect neurogenic mechanisms in order to promote appropriate neurogenesis and the structural and functional recovery of those damages that are produced on the nervous tissue under different neuropathologies, as reviewed above.
73-31-4 Process route
-
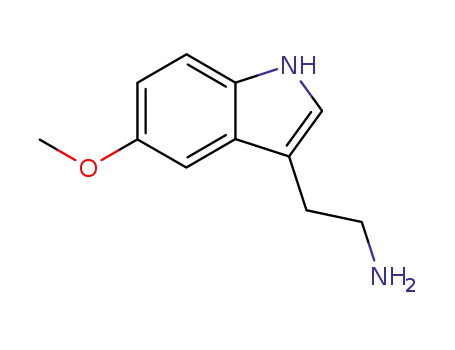
- 608-07-1
2-(5-methoxyindol-3-yl)ethylamine
-
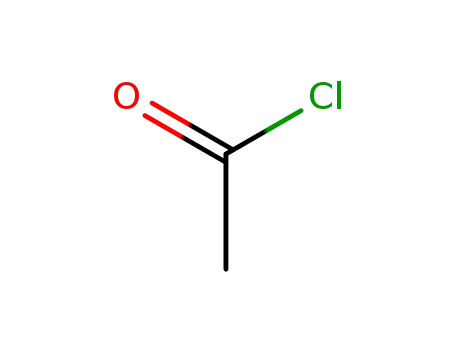
- 75-36-5
acetyl chloride

-
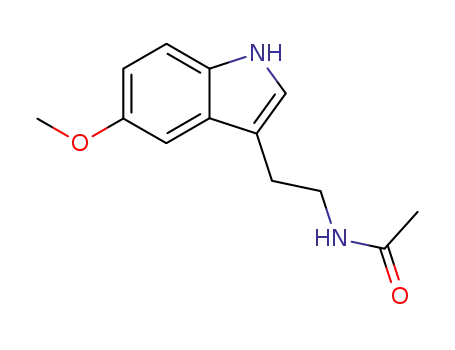
- 73-31-4
5-methoxy-N-acetyl-tryptamine
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
In dichloromethane; at 25 - 30 ℃; Temperature;
|
98.3% |
|
With triethylamine; In toluene; at 8 - 20 ℃; for 7.5h; Inert atmosphere;
|
92.6% |
|
With triethylamine; In dichloromethane; at 20 ℃;
|
|
|
With triethylamine; In dichloromethane; at 0 - 20 ℃; for 5h;
|
-
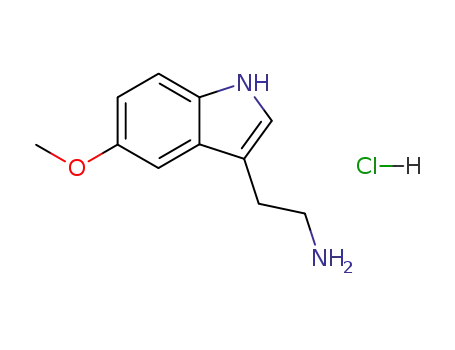
- 66-83-1
5-methoxytryptamine hydrochloride

-
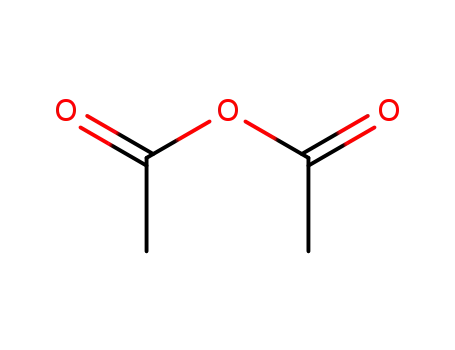
- 108-24-7
acetic anhydride

-

- 73-31-4
5-methoxy-N-acetyl-tryptamine
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With triethylamine; In dichloromethane; at 0 - 25 ℃; for 3h;
|
90% |
73-31-4 Upstream products
-
2436-17-1
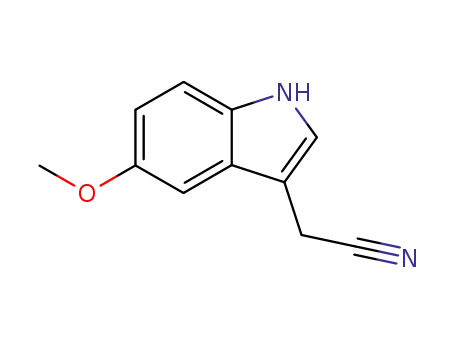
5-methoxyindole-3-acetonitrile
-
188396-98-7
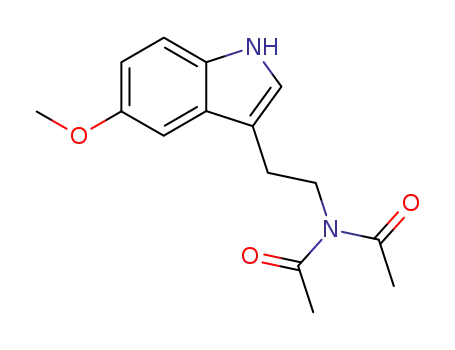
Nb,Nb-diacetyl-5-methoxytryptamine
-
19501-58-7
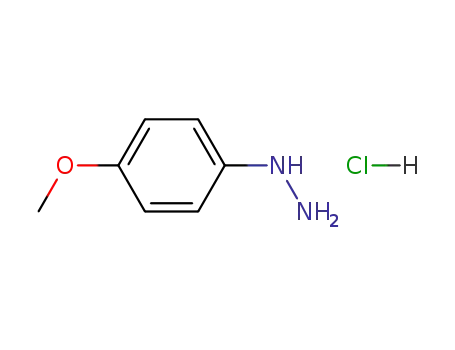
4-methoxyphenylhydrazine hydrochloride
-
63050-21-5
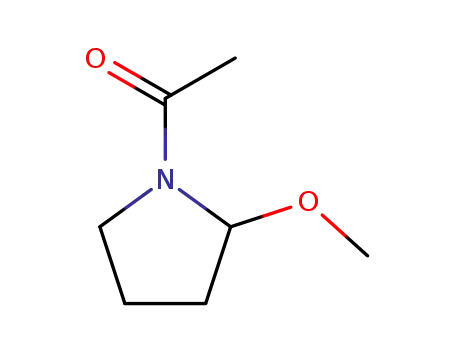
N-acetyl-2-methoxypyrrolidine
73-31-4 Downstream products
-
28772-49-8
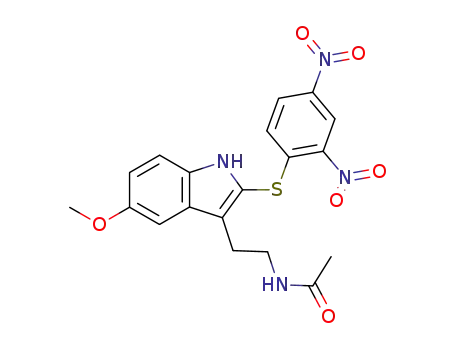
2-(2,4-dinitrophenylsulfenyl)melatonin
-
362-43-6
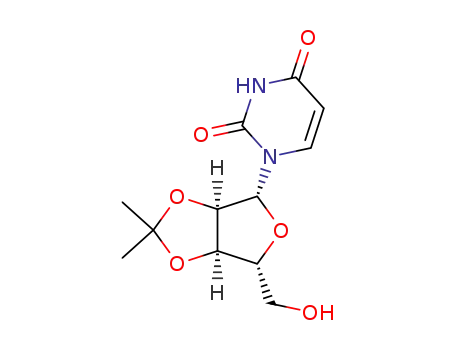
2',3'-O-isopropylideneuridine
-
68798-00-5
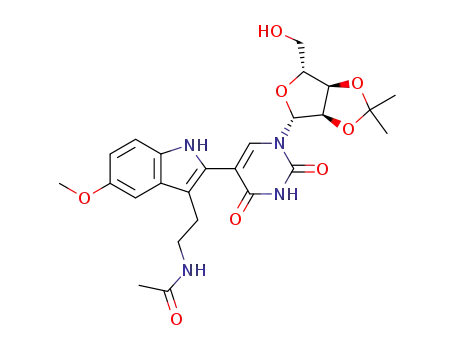
5-<3-<2-(acetylamino)ethyl>-5-methoxy-1H-indol-2-yl>-2',3'-O-(1-methylethylidene)uridine
-
93515-00-5
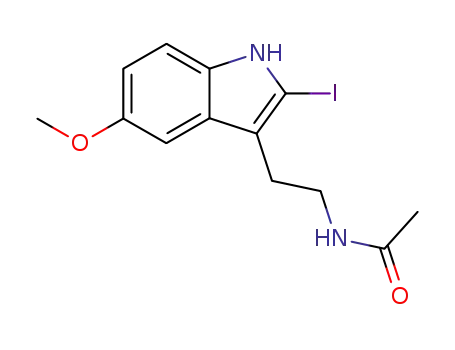
2-iodomelatonin
Relevant Products
-
Cyclopropane, isocyanato- 4747-72-2
CAS:4747-72-2
-
Gemcitabine
CAS:95058-81-4
-
Adenosine
CAS:58-61-7