Product Details
Appearance:White crystalline powder
High Purity Taurine 107-35-7 Good Supplier In China, Fast Delivery
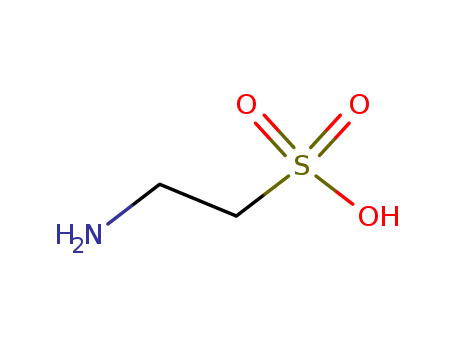
- Molecular Formula:C2H7NO3S
- Molecular Weight:125.148
- Appearance/Colour:White crystalline powder
- Melting Point:>300 °C(lit.)
- Refractive Index:1.515
- PKA:1.5(at 25℃)
- PSA:88.77000
- Density:1.494 g/cm3
- LogP:0.61400
High Purity Taurine 107-35-7 Usage
Taurine is a sulfur-containing amino acid with simple structure in animals. Its chemical name is 2-aminoethanesulfonic acid. Its molecular formula is C2H7NO3S and its molecular weight is 125.15. It is odorless and slightly sour. Reported found in beef, black beans, chicken, chick peas, clams, cod, fish, lamb, milk, octopus, oysters, pistachios, pork, scallops, shrimp and other natural sources.Taurine is an organic acid found in animal tissues and is a major constituent of bile. Disclosed in the present invention is a catalyst for preparing high purity taurine. Taurine has many biological roles such as conjugation of bile acids, antioxidation, osmoregulation, membrane stabilization and modulation of calcium signaling. High urinary levels of taurine may be associated with stress reactions, depression, autism and psychosis.
Definition
ChEBI: An amino sulfonic acid that is the 2-amino derivative of ethanesulfonic acid. It is a naturally occurring amino acid derived from methionine and cysteine metabolism. An abundant component of fish- and meat-based foods, it has been used as an oral suppleme t in the treatment of disorders such as cystic fibrosis and hypertension.
General Description
Large white crystals or white powder.
Air & Water Reactions
Water soluble.
Reactivity Profile
Taurine is an amino acid found in combination with bile acids [Hawley].
Hazard
Toxic by ingestion.
Health Hazard
ACUTE/CHRONIC HAZARDS: Taurine evolves highly toxic fumes when heated to decomposition, and may cause irritation on contact.
Safety Profile
Experimental reproductive effects. Mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of SOx and NOx.
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
Taurine is the most abundant amino acid in the heart. It helps support healthy cardiac rhythm, contraction, and helps support platelet aggregation levels. Taurine has proven beneficial in preventing retinal degeneration and the prevention and treatment of taurine-deficiency dilated cardiomyopathy in cats. Although modern commercial feline diets have added taurine, some cats still develop taurine-deficiency associated dilated cardiomyopathy. It may also be of benefit in taurine (±carnitine) deficient cardiomyopathy in American Cocker Spaniels and certain other breeds such as, Golden Retrievers, Labrador Retrievers, Newfoundlands, Dalmations, Portuguese Water Dogs, and English Bulldogs. Preliminary studies have shown evidence that it may be useful as adjunctive treatment for cardiac disease in animals even if taurine deficiency is not present. Because of its low toxicity, some have suggested it be tried for a multitude of conditions in humans and animals; unfortunately, little scientific evidence exists for these uses.
InChI:InChI=1/C2H7NO3S/c3-1-2-7(4,5)6/h1-3H2,(H-,4,5,6)
107-35-7 Relevant articles
Reactivity and the mechanisms of reactions of β-sultams with nucleophiles
Wood, J. Matthew,Hinchliffe, Paul S.,Laws, Andrew P.,Page, Michael I.
, p. 938 - 946 (2002)
Ethane-1,2-sultam has a pKa of 12.12±0.06 at 30 °C and its rate of alkaline hydrolysis shows a pH-dependence reflecting this so that the observed pseudo first-order rate constant at phs above the pKa are pH independent. A Bronsted plot for this reaction has two distinct correlations with βnuc = 0.52 and 0.65 for weak and strong bases, respectively, although a statistically corrected plot may indicate a single correlation.
Taurine: new implications for an old amino acid
Schuller-Levis Georgia B.,P Eunkyue
, Fems Microbiology Letters 2010/5/10 0:00:00
Taurine is ubiquitous and is the most abundant free amino acid in the heart, retina, skeletal muscle, brain, and leukocytes. Recent molecular studies on the function of taurine provide evidence that taurine is a constituent of biologic macromolecules.
Oxyhalogen-sulfur chemistry - Kinetics and mechanism of the bromate oxidation of cysteamine
Morakinyo, Moshood K.,Chikwana, Edward,Simoyi, Reuben H.
, p. 416 - 425 (2008)
The kinetics and mechanism of the oxidation of the biologically important molecule, cysteamine. by acidic bromate and molecular bromine have been studied. The formation of the N-brominated derivatives of taurine is reversible, with taurine regenerated in the presence of a reducing agent such as iodide. This feature makes it possible for taurine to moderate hypobromous acid toxicity in the physiological environment.
PROCESS SULFONATION OF AMINOETHYLENE SULFONIC ESTER TO PRODUCE TAURINE
-
Paragraph 0030-0031, (2021/06/04)
A process comprises continuously adding a first stream and a second stream to a sulfonation vessel, wherein the first stream comprises aminoethanol sulfate ester (AES) and the second stream comprises an aqueous solution of sodium sulfite (Na2SO3). In an aspect, the AES has a residence time of no more than four hours in the sulfonation vessel. In an aspect the heating step is conducted at a temperature of at least 115° C and a pressure of at least 200 psi.
107-35-7 Process route
-
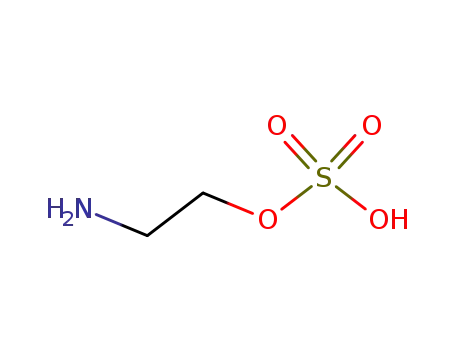
- 926-39-6
sulfuric acid mono-(2-amino-ethyl ester)
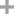
-
- 124-38-9,18923-20-1
carbon dioxide

-
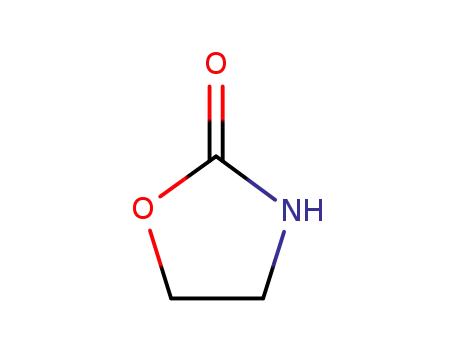
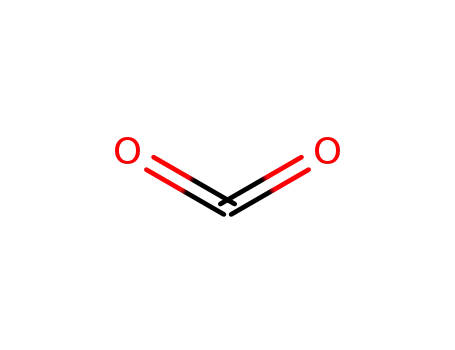
- 497-25-6
dimethylenecyclourethane

-
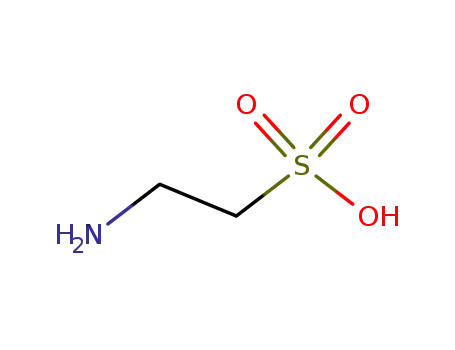
- 107-35-7
Tau

-
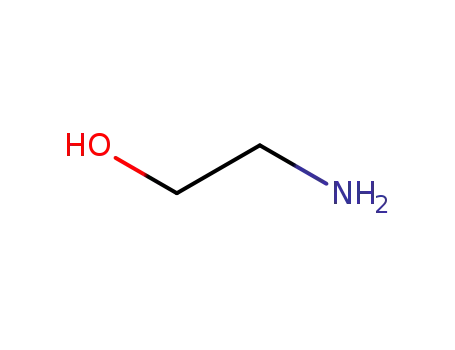
- 141-43-5
ethanolamine
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With sodium hydrogensulfite; sodium hydroxide; In water; at 150 ℃; for 1.5h; under 10343.2 Torr; Inert atmosphere;
|
58% 20% 20% |
-
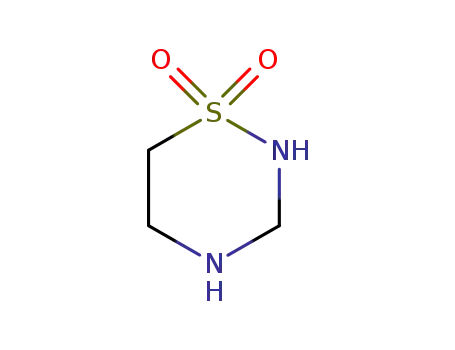
- 38668-01-8
Taurultam

-
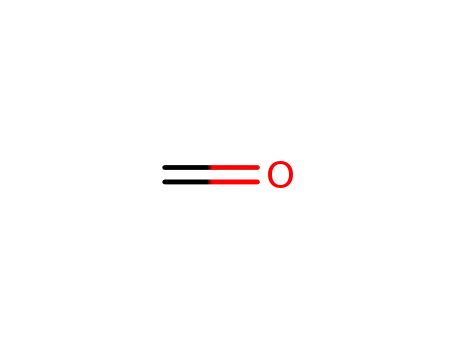
- 50-00-0,30525-89-4,61233-19-0
formaldehyd

-
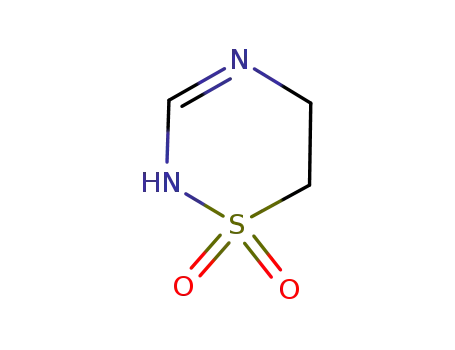
-
dehydrotaurultam

-

- 107-35-7
Tau

-
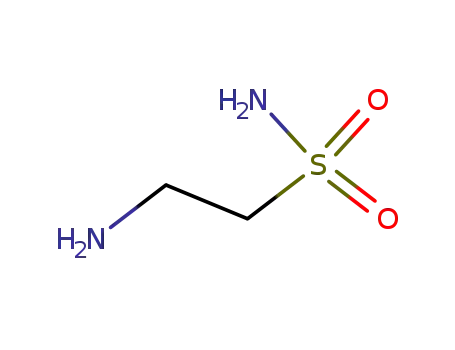
- 4378-70-5
2-aminoethanesulfonamide

-

- 124-38-9,18923-20-1
carbon dioxide
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With water; Product distribution / selectivity; γ-Irradiation;
|
107-35-7 Upstream products
-
926-39-6

sulfuric acid mono-(2-amino-ethyl ester)
-
44826-45-1
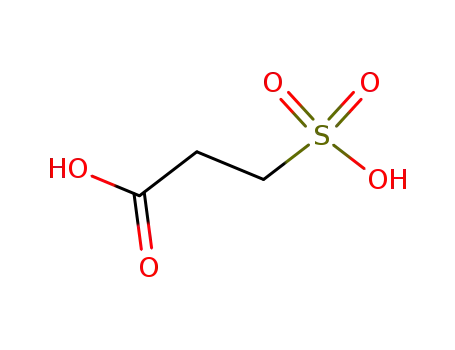
3-sulfopropanoic acid
-
13100-82-8
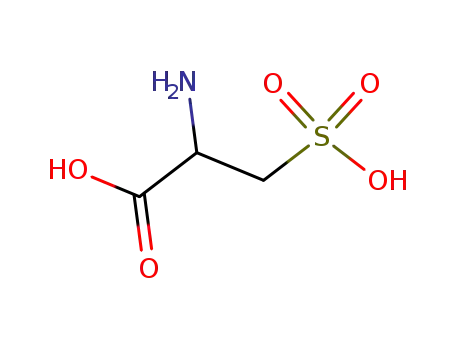
cysteic acid
-
498-40-8
L-Cysteic acid
107-35-7 Downstream products
-
10191-18-1
2-(di(2-hydroxyethyl)amino)ethanesulfonic acid
-
7465-57-8
2-(N,N,N-trimethylamino)ethanesulfonate
-
4443-24-7
NCS 731
-
543-18-0
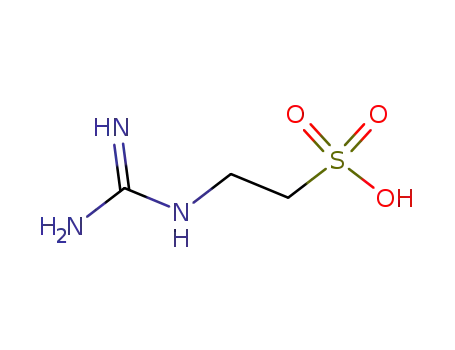
taurocyamine
Relevant Products
-
Sparteine sulfate anhydrous
CAS:299-39-8
-
Acotiamide HCl
CAS:773092-05-0
-
Rocuronium bromide
CAS:119302-91-9