Product Details
Appearance:White fine powder
Wholesaler 87-78-5 Mannitol trader with best price
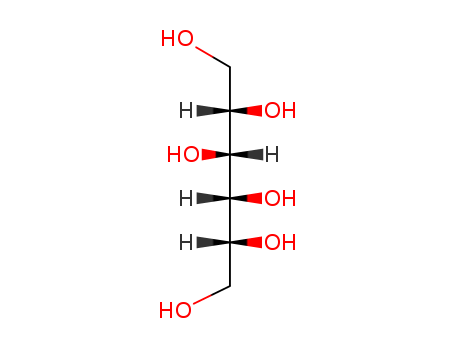
- Molecular Formula:C6H14O6
- Molecular Weight:182.174
- Appearance/Colour:White fine powder
- Vapor Pressure:7.22E-12mmHg at 25°C
- Melting Point:166-168oC
- Refractive Index:1.597
- Boiling Point:494.9 °C at 760 mmHg
- PKA:pKa 13.50(H2O,t =18)(Approximate)
- Flash Point:292.5 °C
- PSA:121.38000
- Density:1.596 g/cm3
- LogP:-3.58540
Mannitol 87-78-5 Usage
Mannitol also known as wood mellow, is a polyol (polyhydric alcohol) produced from hydrogena- tion from fructose that functions as a sweetener, humectant, and bulking agent. It can be used to lower intraocular pressure and in the postoperational period in ophthalomological procedures as well as during brain edema. In the United States, mannitol produced by hydrogenation of glucose or fructose solutions or by fermentation by Zygosaccharomyces rouxii or Lactobacillus intermedius is approved for several food applications. It is also approved in many other countries. Mannitol is the agent most commonly used as an osmotic diuretic.
Production Methods of Mannitol
Mannitol is a good diuretic in medicine. There are two main processes for industrial production of mannitol in the world. One is to take kelp as raw material. One is obtained from sucrose and glucose by hydrolysis, differential isomerization and enzyme isomerization, and then hydrogenation. China has used kelp to extract mannitol for decades.
Definition
A polyhydric alcohol,CH2OH(CHOH)4CH2OH, derived frommannose or fructose. A soluble hexahydric alcohol that occurs in many plants and fungi. It is used in medicines and as a sweetener (particularly in foods for diabetics). It is an isomer of sorbitol.
Safety Profile
A poison by intravenous route. Human systemic effects. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating vapors.
InChI:InChI=1/C6H14O6/c7-1-3(9)5(11)6(12)4(10)2-8/h3-12H,1-2H2/t3-,4-,5-,6+/m0/s1
87-78-5 Relevant articles
Direct conversion of cellulose into isosorbide over Ni doped NbOPO4catalysts in water
Guo, Jiaxing,He, Minyao,Li, Cuiqing,Liu, ShanShan,Song, Yongji,Wang, Hong,Wang, Xincheng
supporting information, p. 10292 - 10299 (2020/07/14)
In this study, bifunctional catalysts based on niobium phosphates were prepared by a facile hydrothermal method and used for the direct conversion of cellulose to isosorbide under aqueous conditions. This study provides as an efficient strategy for the development of novel multifunctional heterogeneous catalysts for the one-pot valorisation of cellulose. This journal is
Role of the Strong Lewis Base Sites on Glucose Hydrogenolysis
Yazdani, Parviz,Wang, Bo,Gao, Feng,Kawi, Sibudjing,Borgna, Armando
, p. 3845 - 3853 (2018/07/31)
This work reports the individual role of strong Lewis base sites on catalytic conversion of glucose hydrogenolysis to acetol/lactic acid, including glucose isomerisation to fructose and pyruvaldehyde rearrangement/hydrogenation to acetol/lactic acid. Las
Hydrothermally Stable Ruthenium–Zirconium–Tungsten Catalyst for Cellulose Hydrogenolysis to Polyols
Lucas, Martin,Fabi?ovicová, Katarina,Claus, Peter
, p. 612 - 618 (2017/12/28)
In this work, we describe a catalytic material based on a zirconium–tungsten oxide with ruthenium for the hydrogenolysis of microcrystalline cellulose under hydrothermal conditions. The prepared Zr-W oxide is mesoporous and largely stable under hydrothermal conditions (493 K and 65 bar hydrogen). Decomposition into the components ZrO2 and WO3 could be observed at temperatures of 1050 K in air.
87-78-5 Process route
-
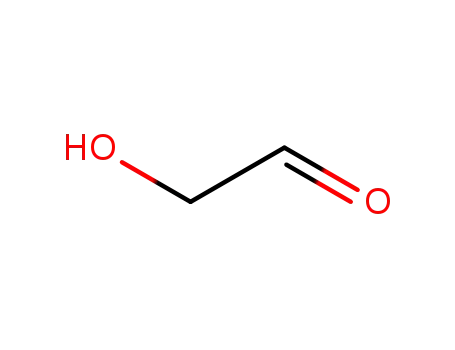
- 141-46-8
Glycolaldehyde

-
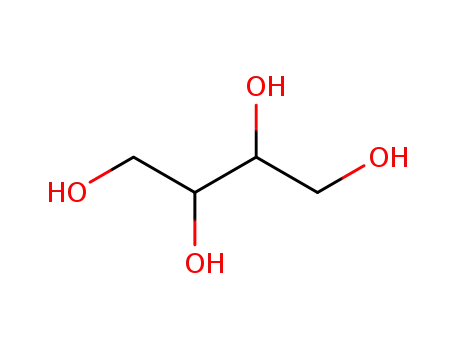
- 2319-57-5,2418-52-2,6968-16-7,7493-90-5,7541-59-5,10030-58-7,188346-77-2,149-32-6
1,2,3,4-butanetetrol
-
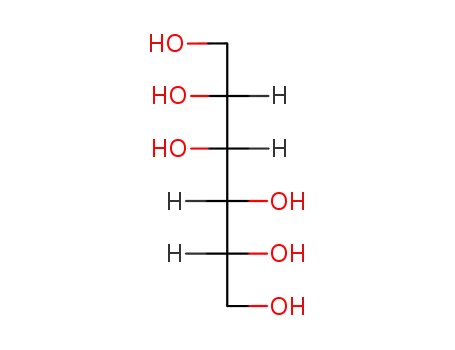
- 50-70-4,69-65-8,87-78-5,133-43-7,488-44-8,488-45-9,608-66-2,643-01-6,643-03-8,5552-13-6,6706-59-8,24557-79-7,25878-23-3,26566-34-7,45007-61-2,60660-56-2,60660-57-3,60660-58-4,132747-27-4
sorbitol
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
Glycolaldehyde; With L-proline; In water; at 20 ℃;
With sodium tetrahydroborate; In methanol; at 0 ℃; Title compound not separated from byproducts;
|
-
cellulose
- 9004-34-6
cellulose

-
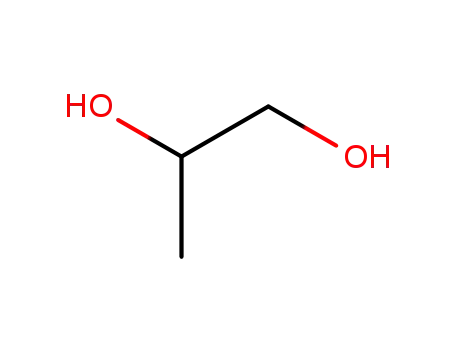
- 57-55-6,63625-56-9
propylene glycol

-

- 2319-57-5,2418-52-2,6968-16-7,7493-90-5,7541-59-5,10030-58-7,188346-77-2,149-32-6
1,2,3,4-butanetetrol

-
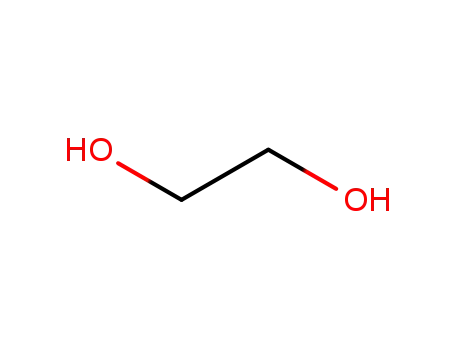
- 107-21-1
ethylene glycol

-

- 50-70-4,69-65-8,87-78-5,133-43-7,488-44-8,488-45-9,608-66-2,643-01-6,643-03-8,5552-13-6,6706-59-8,24557-79-7,25878-23-3,26566-34-7,45007-61-2,60660-56-2,60660-57-3,60660-58-4,132747-27-4
sorbitol
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With hydrogen; In water; at 199.84 ℃; for 0.5h; under 45004.5 Torr; Autoclave;
|
87-78-5 Upstream products
-
50-70-4
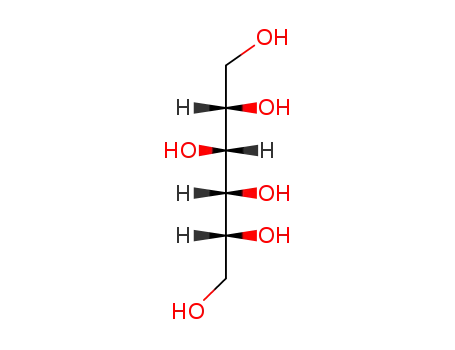
D-sorbitol
-
50-99-7
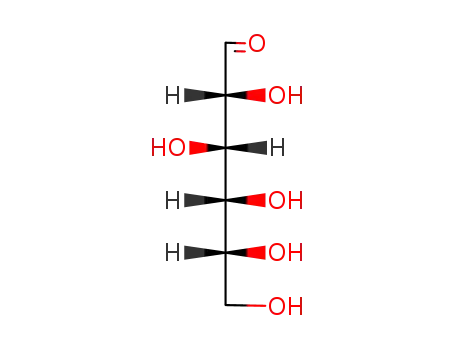
D-glucose
-
643-03-8
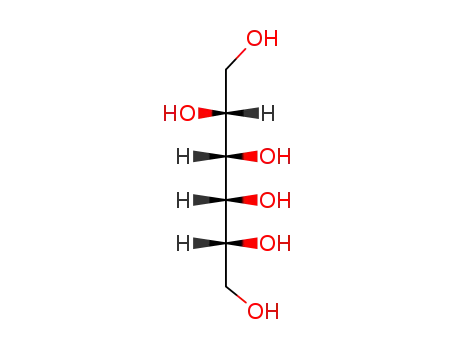
D-talitol
-
60660-58-4
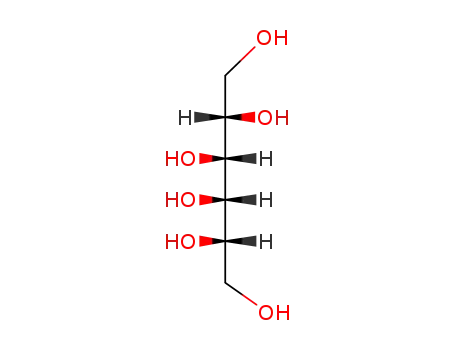
L-altritol
87-78-5 Downstream products
-
642-00-2
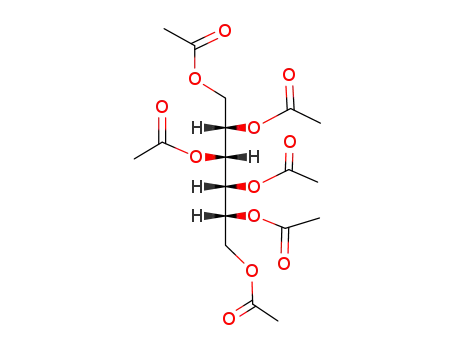
DL-glucitol hexa-acetate
-
3530-21-0
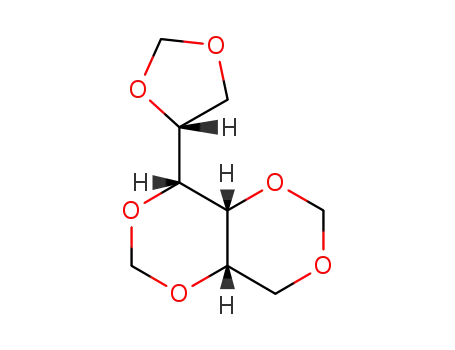
O1,O3;O2,O4;O5,O6-trimethanediyl-DL-glucitol
-
57-55-6

propylene glycol
-
116-09-6
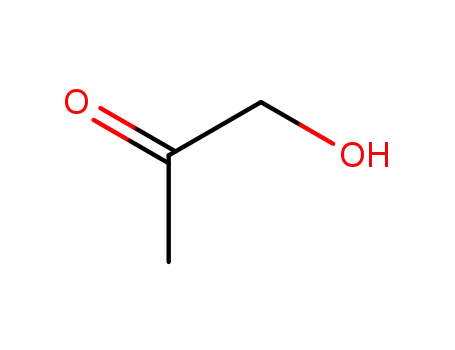
hydroxy-2-propanone
Relevant Products
-
1,2,6,7-Tetrahydro-8H-indeno[5,4-b]furan-8-one 196597-78-1
CAS:196597-78-1
-
Ergosterol
CAS:57-87-4
-
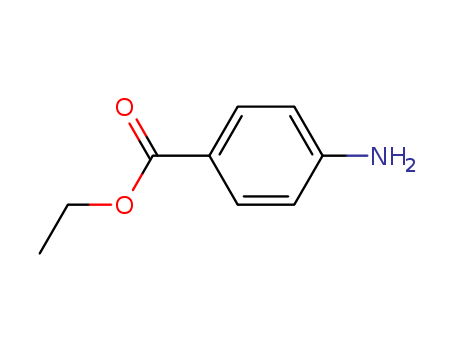
Benzoicacid, 4-amino-, ethyl ester
CAS:94-09-7