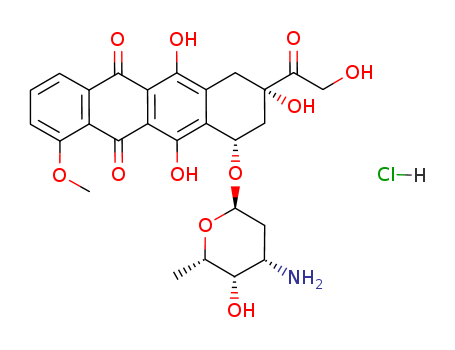
25316-40-9
- Product Name:Doxorubicin hydrochloride
- Molecular Formula:C27H30ClNO11
- Purity:99%
- Molecular Weight:
Product Details
Appearance:orange-red crystalline solid
Hot Sale Doxorubicin hydrochloride 25316-40-9 in stock, good producer
- Molecular Formula:C27H30ClNO11
- Molecular Weight:579.988
- Appearance/Colour:orange-red crystalline solid
- Vapor Pressure:9.64E-28mmHg at 25°C
- Melting Point:216 °C (dec.)(lit.)
- Boiling Point:810.3 °C at 760 mmHg
- PKA:pKa 8.25±0.60 (Uncertain);8.43±0.70 (Uncertain);11.9±0.4 (Uncertain);12.95±0.1 (Uncertain);13.8±0.70 (Uncertain)
- Flash Point:443.8 °C
- PSA:206.07000
- LogP:1.50360
Doxorubicin hydrochloride 25316-40-9 Usage
Doxorubicin (DXR) is a clinically important cancer chemotherapeutic agent and, in spite of undesirable acute and long-term toxic effects, DXR remains one of the most widely used antitumor drugs because of its broad spectrum of activity[1]. DXR was first isolated in 1969[1] from Streptomyces peucetius subsp caesius ATCC 27952, a higher DXR-producing mutant strain derived from the wild-type S. peucetius ATCC 29050 strain, and is formed by C-14 hydroxylation of its immediate precursor, DNR. It is a potent antitumour agent active against a wide spectrum of malignancies, including leukaemias, sarcomas, breast cancer, small cell lung cancer and ovarian cancer. Doxorubicin is used to produce regression in disseminated neoplastic conditions like acute lymphoblastic leukemia, acute myeloblastic leukemia, Wilms’ tumor, neuroblastoma, soft tissue and bone sarcomas, breast carcinoma, ovarian carcinoma, transitional cell bladder carcinoma, thyroid carcinoma, gastric carcinoma, Hodgkin's disease, malignant lymphoma and bronchogenic carcinoma in which the small cell histologic type is the most responsive compared to other cell types. Doxorubicin is also indicated for use as a component of adjuvant therapy in women with evidence of axillary lymph node involvement following resection of primary breast cancer. A detailed study of the mechanisms involved in doxorubicin-induced changes in membrane structure and function has not been undertaken. However, doxorubicin binds to the epidermal growth factor receptor at clinically relevant drug concentrations, and alters its function.
Chemical Properties
Doxorubicin is an orange to red cake-like or needle-like crystalline solid. It is a cytotoxic anthracycline antibiotic isolated from cultures of Streptomyces peucetius var. caesius. Doxorubicin hydrochloride is an orange-red, crystalline, hygroscopic powder that is soluble in water and slightly soluble in methanol.
Originator
Adriblastina,Farmitalia,Italy,1971
Brand name
Adriamycin (Pharmacia & Upjohn); Doxil (ALZA); Rubex (Bristol-Myers Squibb).
Biological Functions
The C13 substituent of doxorubicin is hydroxymethyl, which retards the action of cytosolic aldoketoreductase and slows the conversion to the equally active, but chronically cardiotoxic, doxorubicinol.
Fire Hazard
Doxorubicin hydrochloride is probably combustible.
Biological Activity
Antitumor antibiotic agent that inhibits DNA topoisomerase II. DNA intercalator that inhibits nucleic acid synthesis and induces apoptosis.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Naturally fluorescent anthracycline antibiotic, anticancer drug. Doxorubicin is a substrate of MRP1 which was first cloned from a DOX-resistant lung cancer cell line. Fluorescent property has been exploited for the measurement of drug efflux pump activities as well as resolving the important question of intracellular localization of various multidrug resistance proteins and the role of subcellular organelles (Golgi and lysosome) in the sequestration of drugs and its implication in drug resistant phenotypes.
Shipping
UN2811 Toxic solids, organic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required.
Incompatibilities
Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides
Waste Disposal
It is inappropriate and possibly dangerous to the environment to dispose of expired or waste pharmaceuticals by flushing them down the toilet or discarding them to the trash. Household quantities of expired or waste pharmaceuticals may be mixed with wet cat litter or coffee grounds, double-bagged in plastic, discard in trash. Larger quantities shall carefully take into consideration applicable DEA, EPA, and FDA regulations. If possible return the pharmaceutical to the manufacturer for proper disposal being careful to properly label and securely package the material. Alternatively, the waste pharmaceutical shall be labeled, securely packaged and transported by a state licensed medical waste contractor to dispose by burial in a licensed hazardous or toxic waste landfill or incinerator.
InChI:InChI=1/C27H29NO11.ClH/c1-10-22(31)13(28)6-17(38-10)39-15-8-27(36,16(30)9-29)7-12-19(15)26(35)21-20(24(12)33)23(32)11-4-3-5-14(37-2)18(11)25(21)34;/h3-5,10,13,15,17,22,29,31,33,35-36H,6-9,28H2,1-2H3;1H/t10-,13-,15-,17-,22+,27-;/m0./s1
25316-40-9 Relevant articles
Reversing the undesirable pH-profile of doxorubicin: Via activation of a di-substituted maleamic acid prodrug at tumor acidity
Zhang, Anqi,Yao, Lan,An, Ming
, p. 12826 - 12829 (2017)
The acid-labile behavior of di-substituted maleamic acid (DMA) and its equilibrium with di-substituted maleimide (DMI) are exploited to build an ultra acid-sensitive, small molecule prodrug that can be activated by tumor extracellular pH (pHe) in the range of 6.5-6.9. Such a DMA prodrug reversed the unfavorable pH-profile of doxorubicin (Dox), which may improve its therapeutic window.
ADIPOCYTE MEDIATED DELIVERY OF ANTICANCER THERAPEUTICS
-
Page/Page column 29, (2020/05/28)
Disclosed are compositions and methods related to the use of adipocytes for sustained release of anti-cancer therapeutics and treatment of cancer.
CHANNEL PROTEIN ACTIVATABLE LIPOSOMES
-
Page/Page column 112, (2014/06/11)
The liposomes are used in a kit comprising the liposome, the liposomal membrane of which comprises a channel protein linked to a Trigger, and an Activator for the Trigger, wherein the Trigger comprises the eight- membered non-aromatic cyclic alkenylene group, and the Activator comprises a diene.
25316-40-9 Process route
-
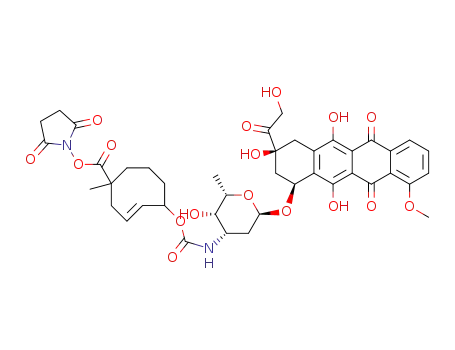
-
doxorubicin

-
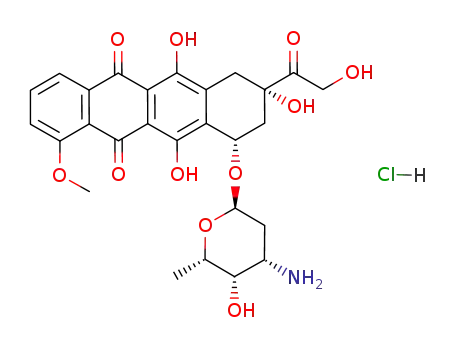
- 25316-40-9
doxorubicin hydrochloride
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With 3,6-dimethyl-1,2,4,5-tetrazine; In acetonitrile; Reagent/catalyst;
|
|
|
With 3,6-dimethyl-1,2,4,5-tetrazine; In acetonitrile; Reagent/catalyst;
|
-
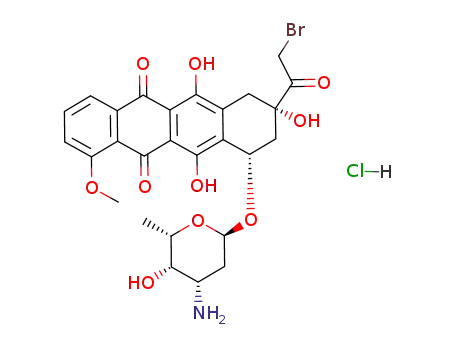
- 29742-67-4
14-bromodaunorubicin hydrochloride

-

- 25316-40-9
doxorubicin hydrochloride
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
In water; dimethyl sulfoxide; at 80 ℃; for 2h;
|
64% |
25316-40-9 Upstream products
-
29742-67-4

14-bromodaunorubicin hydrochloride
-
23541-50-6
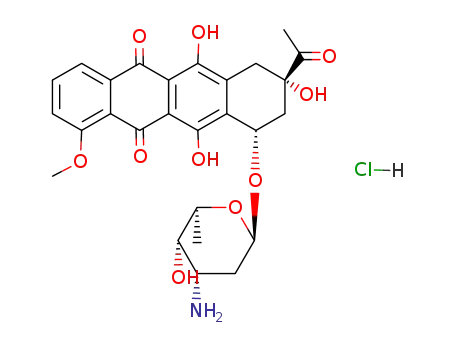
daunomycin hydrochloride
25316-40-9 Downstream products
-
89164-77-2
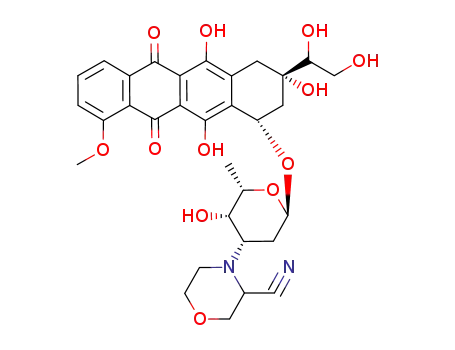
3'-deamino-3'-(3-cyano-4-morpholinyl)-13-dihydrodoxorubicin
-
80875-73-6
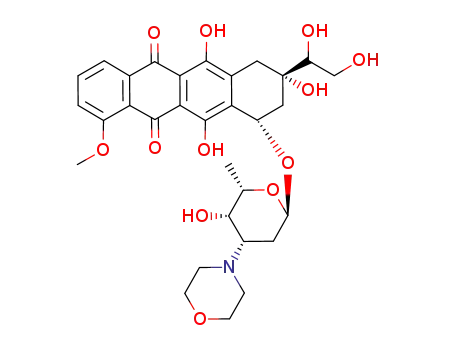
3'-deamino-3'-(4-morpholinyl)-13-dihydrodoxorubicin
-
80790-68-7
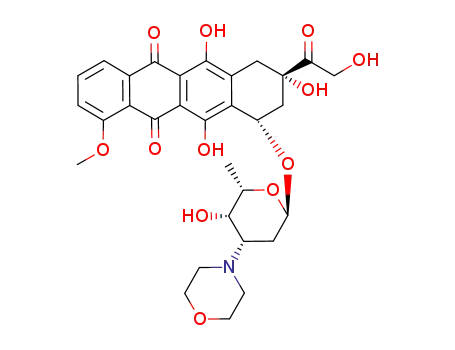
3'-deamino-3'-(4-morpholinyl)doxorubicin
-
88254-07-3
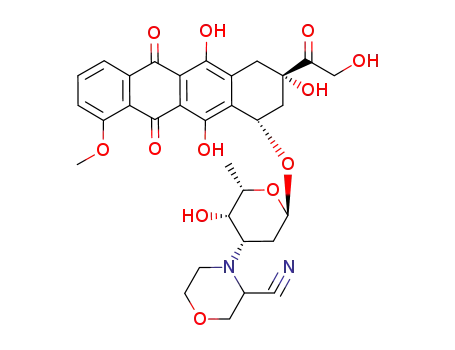
3'-deamino-3'-(3-cyano-4-morpholinyl)doxorubicin
Relevant Products
-
5-Chloro-2-nitrodiphenylamine
CAS:25781-92-4
-
17-Methyltestosterone
CAS:58-18-4